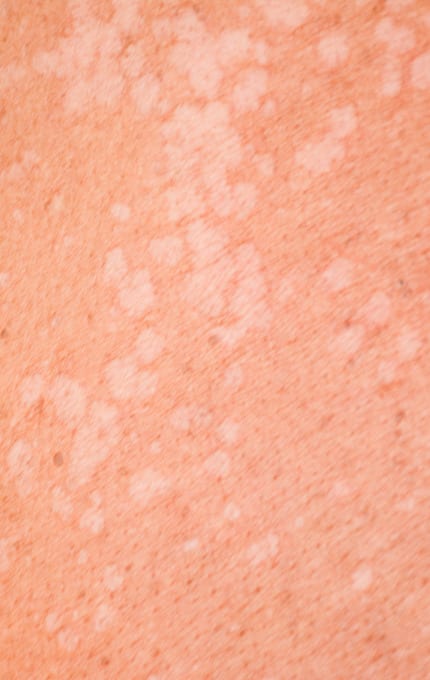
Versicolor tinea is a fungal disease that does not cause visible inflammatory reactions on the skin. It belongs to the group of keratomycosis. The causative agent of the disease is Phitosporum orbiculare, which parasitize in the uppermost parts of the horny layer of the skin. The most vulnerable areas of the skin, susceptible to affection by versicolor tinea, are the areas of the chest, back, axillary cavity. If the disease is not treated for a long time, the foci can move to the shoulders, abdomen and side surfaces.
Statistically, versicolor tinea in our climate affects up to 5–10% of the population.
With versicolor tinea, yellow rashes are formed. In some cases, the places of inflammation are of dark brown colour. The fungus affects first of all the horny layer of epidermis, which leads to peeling of the skin areas affected by the pity scales. When scraping the skin, these scales easily separate, but with frequent washing, they are practically invisible. Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, there is an intense peeling of the affected skin. This method in some cases contributes to the complete cure of the patient.