Oily skin is a type of skin caused by excessive activity of the sebaceous glands and is characterized by a rough texture, unhealthy color and gloss.
Signs of oily skin
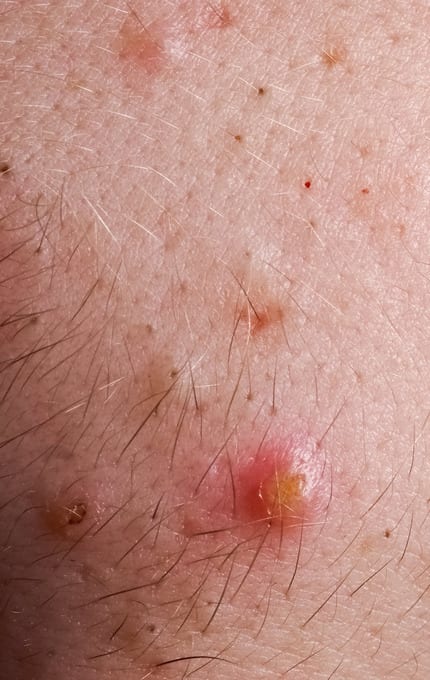
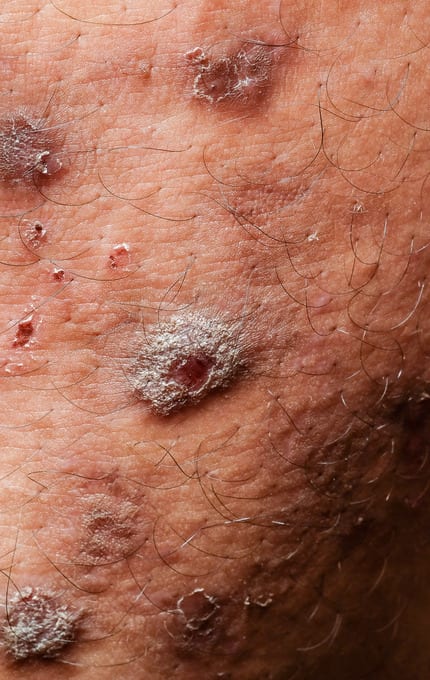
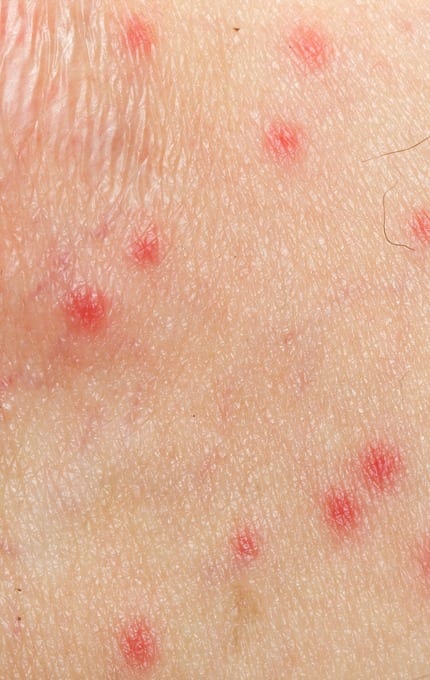
This type of skin often combines several cosmetic flaws. In addition to such a common symptom as an unaesthetic shine and a tendency to rapid contamination, oily skin suffers from a number of other problems. The pores on such skin are easily clogged with sebum, dirt and makeup residues, contributing to the appearance of comedones – clogged sebaceous glands. Under the influence of oxygen, sebum oxidizes and stains the clogged pores in a dark color: the result is such a cosmetic defect as “black dots”.
The individual structural features of the sebaceous glands, local skin immunity, the general condition of the body and many other factors play an important role in the development of various skin inflammations on oily skin. And clogged pores can be transformed into small pimples and subcutaneous inflamed nodes and abscesses. In complex cases, excessive oily skin can be combined with increased skin reactivity. Oily sensitive skin can suffer both from inflammatory processes and from intolerance to therapeutic seborrhea, antiseptic, drying agents. Therefore, such a skin requires a strictly individual approach.
Oily skin is determined by several factors:
- heredity
- hormonal imbalance
- stress
- environmental pollution
- bad habits and poor diet
- improperly selected cosmetic care
- climatic changes
In case of acne, you should visit a dermatologist. And if oily skin is accompanied by the appearance of unwanted hairs, then check the hormonal background: perhaps the problems are associated with the level of certain hormones, and they should be solved by a specialist.